In rural India, where opportunities for women are often limited, the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act MGNREGA stands as a beacon of hope. This landmark scheme guarantees 100 days of wage employment to every rural household, prioritizing womens participation. For millions of female workers, MGNREGA is more than a jobits a pathway to financial independence, dignity, and social change.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!This blog dives deep into how MGNREGA empowers women in rural areas. Well explore its benefits, challenges, and real-life impacts while answering common questions and sharing inspiring stories. Lets uncover why MGNREGA is a cornerstone of womens empowerment in India.

What Is MGNREGA
Understanding the Scheme
MGNREGA, launched in 2005, is one of Indias largest social welfare programs. It guarantees 100 days of unskilled manual work per year to rural households, with a focus on inclusive growth. The scheme emphasizes creating durable community assets like roads, canals, and water conservation structures.
Women are a priority under MGNREGA, with at least one-third of jobs reserved for them. This ensures female workers have access to employment opportunities. The program operates in every Indian state, reaching even the most remote villages.
Key Objectives for Rural Empowerment
MGNREGA aims to reduce poverty and unemployment in rural areas. It promotes sustainable development by building infrastructure that benefits communities long-term. For women, the scheme offers a chance to earn wages, gain skills, and contribute to village progress.
The focus on gender equity makes MGNREGA unique. By prioritizing womens participation, it tackles systemic barriers like economic dependence and social exclusion. Its a tool for both economic and social empowerment.
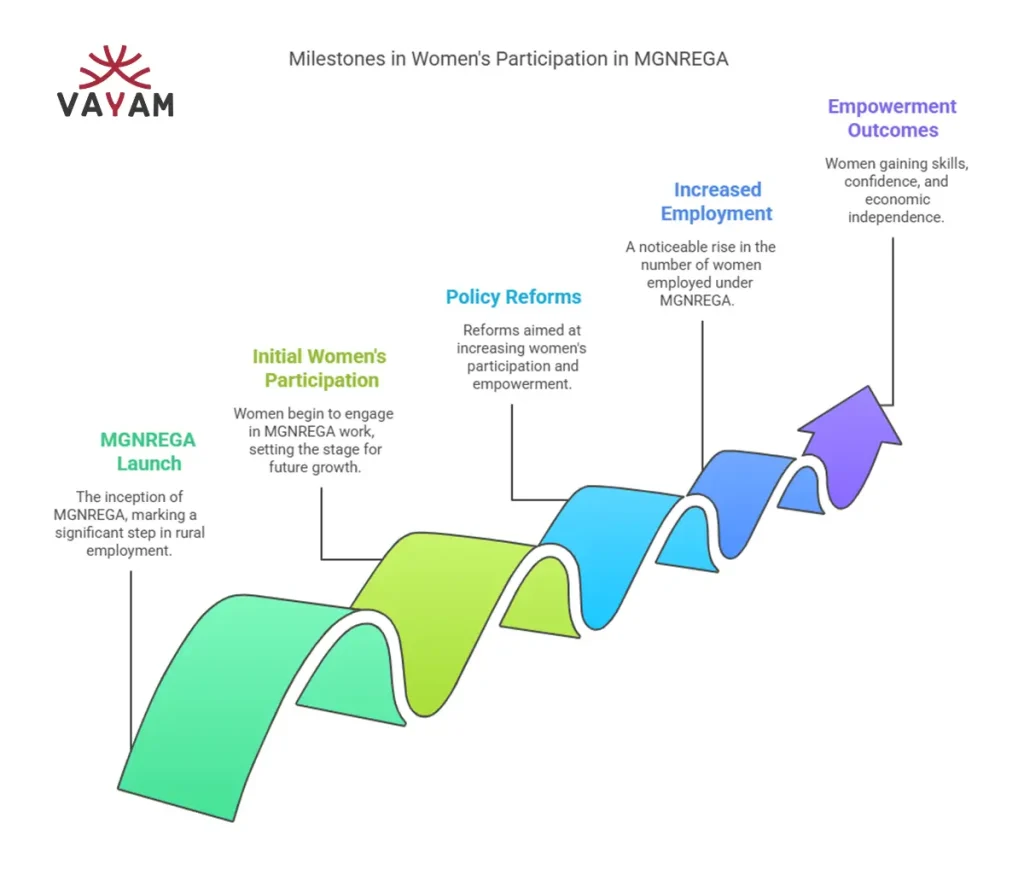
Women in MGNREGA A Game-Changer
Participation Trends
Women make up over 50 of MGNREGAs workforce in many states. In 2023-24, women accounted for 56 of the total person-days worked, a significant rise from earlier years. This trend reflects growing awareness and accessibility for female workers.
States like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Rajasthan lead in womens participation. These numbers show MGNREGAs success in mobilizing rural women. Yet, participation varies by region due to cultural and logistical factors.
Economic Independence for Rural Women
For many women, MGNREGA is their first source of independent income. Wages earned through the scheme help them support their families, pay for education, or save for emergencies. This financial autonomy reduces reliance on male breadwinners.
Economic independence also boosts confidence. Women who work under MGNREGA often take on leadership roles in their communities. The scheme is reshaping gender dynamics in rural India, one paycheck at a time.

How MGNREGA Empowers Female Workers
Financial Security and Livelihoods
MGNREGA provides a safety net during lean agricultural seasons. Women earn minimum wages, ensuring a steady income for household needs. This stability is critical in areas with limited job opportunities.
Direct bank transfers ensure transparency and security. Women no longer depend on intermediaries, reducing exploitation. Financial security empowers them to make decisions about spending and savings.
Skill Development Opportunities
MGNREGA offers more than manual labor. Women learn skills like masonry, water management, and horticulture through worksite projects. These skills enhance employability beyond the scheme.
Training programs under MGNREGA also promote leadership. Women are encouraged to become worksite supervisors or trainers. Such opportunities build long-term career prospects.
Social Empowerment and Community Impact
MGNREGA fosters a sense of agency among women. Working alongside men, they challenge stereotypes about womens roles. Their contributions to community assets like roads and schools earn respect.
The scheme also encourages collective action. Women form self-help groups to advocate for better wages or facilities. This solidarity strengthens their voice in village governance.
Challenges Faced by Women in MGNREGA
Wage Disparities
Despite equal pay mandates, women sometimes earn less than men for similar work. In some areas, tasks assigned to women are undervalued, leading to lower wages. Addressing this gap requires stricter enforcement.
Delayed wage payments also affect women disproportionately. Many rely on timely earnings for daily expenses. Improving payment systems is crucial for fairness.
Access to Worksite Facilities
Worksites often lack basic amenities like childcare, drinking water, or toilets. This discourages women, especially mothers, from participating fully. Providing these facilities would boost attendance.
Safety concerns at remote worksites are another barrier. Women need secure transport and protective measures. Local authorities must prioritize these issues.
Social and Cultural Barriers
Patriarchal norms restrict womens mobility in some regions. Families may discourage female participation due to traditional expectations. Community awareness campaigns can help shift mindsets.
Caste and class dynamics also create exclusion. Marginalized women face discrimination in job allocation. Inclusive policies are needed to ensure equal access.

Read More
How to Volunteer for Organizations Fighting Child Labour
10 Corporate Leaders Who Are Changing the CSR Game for NGOs
People In addition Ask Common Questions About MGNREGA for Women
How does MGNREGA benefit women specifically?
MGNREGA offers women stable income, skill-building, and social recognition. It reduces economic dependence and promotes gender equity. Women gain confidence and contribute to community development.
What percentage of MGNREGA workers are women?
As of 2023-24, women make up about 56 of MGNREGAs workforce. This varies by state, with higher participation in southern and western regions. The schemes gender focus drives these numbers.
Are women paid equally under MGNREGA?
MGNREGA mandates equal pay for equal work. However, disparities occur due to task valuation or delays. Stronger monitoring can ensure women receive fair wages.
How does MGNREGA promote gender equality?
The scheme reserves at least one-third of jobs for women and encourages their leadership. It challenges traditional roles by providing economic and social opportunities. Womens contributions reshape community perceptions.
What challenges do women face in MGNREGA?
Women face wage delays, inadequate worksite facilities, and cultural barriers. Safety concerns and discrimination also hinder participation. Policy reforms can address these issues effectively.
Success Stories Women Thriving Through MGNREGA
Case Study Transforming Lives in Rajasthan
In Rajasthans Dungarpur district, Sunita Devi led a group of women to build a village pond under MGNREGA. The pond now supports irrigation and fishing, boosting local incomes. Sunitas leadership earned her a role as a panchayat member.
Her story shows how MGNREGA empowers women to drive change. From laborer to leader, Sunitas journey inspires others. The pond stands as a symbol of her communitys progress.
Case Study Building Community Assets in Odisha
In Odisha, a group of women constructed a rural road connecting their village to a market. The road cut travel time and increased trade opportunities. The women, trained in masonry, now take on private contracts.
This project highlights MGNREGAs ripple effect. Women gained skills, income, and respect. Their work continues to benefit the entire village.

The Future of MGNREGA for Women
Policy Recommendations
To enhance MGNREGAs impact, policymakers should focus on gender-specific needs. Increasing childcare facilities at worksites would support mothers. Regular audits can ensure equal pay and timely disbursements.
Training programs should expand to include digital literacy and advanced skills. This would prepare women for diverse job markets. Community outreach can address cultural resistance.
Strengthening Gender-Inclusive Measures
MGNREGA can set a global example for gender equity. Introducing quotas for women in supervisory roles would promote leadership. Partnerships with NGOs can provide mentorship and resources.
Technology, like mobile apps for wage tracking, can improve transparency. Empowering women through MGNREGA requires innovation and commitment. The potential is limitless.
Conclusion A Path to Empowerment
MGNREGA is more than an employment schemeits a movement for womens empowerment in rural India. By providing jobs, skills, and social standing, it transforms lives and communities. Despite challenges, its impact is undeniable.
For rural women, MGNREGA offers a chance to dream bigger. With continued reforms, it can pave the way for a more equitable future. Lets celebrate and support this journey toward empowerment.

