
The Right to Education (RTE) Act has been a pivotal step toward ensuring equitable access to quality education for all children in India. Designed to guarantee free and compulsory education to children aged 6 to 14 years, RTE has transformed millions of lives. However, despite its noble intent, many parents face a distressing situation when their child’s RTE application is rejected.
The sting of rejection feels particularly harsh when you believe your child deserves a seat in a government or aided school. You’ve followed all guidelines to the letter, gathered necessary documents, and submitted your application timely, only to discover it’s been denied. The immediate question that comes to mind is what to do next.
Understanding the Basis of an RTE Rejection
Before diving into the appeal process, understanding why your application might have been rejected is crucial. There are several common reasons:
Incomplete or incorrect documentation often tops the list. Even a single missing piece of evidence can lead an admission committee to reject your application.
Late submission is another prevalent cause. Many schools adhere rigidly to cut-off dates, and missing the deadline, even by a day, often results in automatic disqualification.
Some applications are rejected due to errors in eligibility criteria. Parents sometimes misinterpret age limits, residency requirements, or income thresholds, submitting applications when their child isn’t actually eligible.
Finally, there are occasions where rejections might be due to discriminatory practices or arbitrary decisions by school authorities. While illegal and unacceptable, such occurrences do happen.
The Immediate Steps Post-Rejection
Upon receiving a rejection notice, it’s natural to feel frustrated or overwhelmed. However, taking immediate, structured action can make a significant difference.
First, thoroughly review the rejection letter or notice. Many schools provide a brief reason for rejection, which can be a starting point for your appeal.
Next, collect all documentation related to your application. This includes your RTE application form, income certificates, residence proof, age proof, and any correspondence with the school or education department.
Then, understand the timeline for filing an appeal. Different states have different deadlines, usually ranging from 15 to 30 days from the date of rejection. Missing this timeline can severely impact your chances.
Exploring the Formal Appeal Process
India’s RTE Act includes provisions for appealing decisions. Section 19 of the Act and the state-specific RTE rules outline the procedure for handling grievances.
Typically, the first level of appeal is with the school itself. Most states expect parents to first approach the school management committee in writing. This appeal should detail the errors or discrepancies in the rejection decision clearly but respectfully.
If the school rejects your appeal or doesn’t respond within a reasonable timeframe, the next step is approaching the local authority. In most states, this is the District Education Officer (DEO).
Some states have established dedicated RTE grievance redressal officers at the district level, specifically for handling such matters. Ensure you’re aware of the correct officer or office to approach in your area.
The formal appeal to the DEO or concerned authority should be made within the stipulated timeframe. It usually requires submitting a written application along with supporting documents.

How to Draft an Effective Appeal?
Writing a compelling appeal involves clearly stating your case while staying factual and respectful. Here’s a structured way to approach drafting your appeal.
Begin with a formal salutation and clearly state your name, contact details, and the child’s name. Mention the school where you applied and the date your application was rejected.
Clearly articulate why you believe the rejection decision was incorrect. If there was an error in interpreting eligibility criteria, clearly explain this with reference to the RTI Act provisions.
Attach all relevant documents that support your case. If the rejection was due to income criteria, attach an updated income certificate. If it was related to residence, provide additional or corrected address proof.
Ensure your request is specific. Rather than simply asking for reconsideration, specifically request an order directing the school to admit your child.
Conclude respectfully and provide your signature along with the date. Keep copies of all documents and a record of your communications.
People Also Ask:
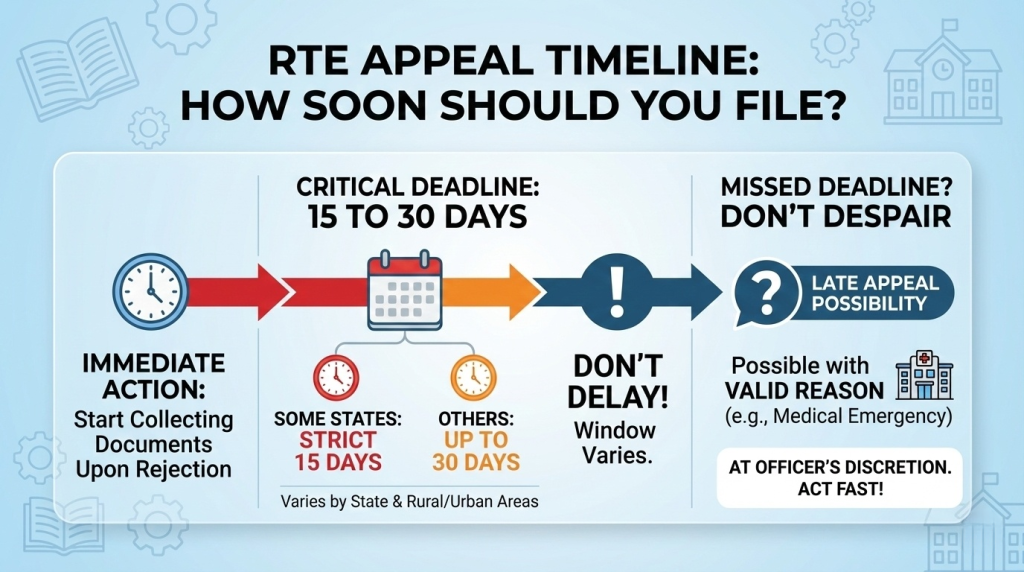
How Soon Should You File an RTE Appeal?
Timing is of critical importance when filing an RTE appeal. Most states have a fixed deadline of 15 to 30 days from the date of rejection to file an appeal with the District Education Officer (DEO).
Some states have stricter timelines of 15 days. Others allow up to 30 days. The window may vary even within a state between rural and urban areas.
It’s essential to act immediately upon receiving rejection. Even if a school delays providing the reason for rejection, begin collecting documents and gathering evidence of your eligibility right away.
If you miss the official deadline, don’t despair. Many states allow for late appeals if a valid reason, such as a medical emergency, can be provided. But these exceptions are at an officer’s discretion.
Can You Use RTI Act When Your RTE Application is Rejected?
The Right to Information (RTI) Act can be a powerful tool when your child’s RTE application is rejected. If the school or DEO does not provide a clear reason for rejection, you can file an RTI application seeking specific information.
Under the RTI Act, you can request the exact grounds for rejection, minutes of the admission committee meetings, and copies of your application’s evaluation.
This information is crucial to draft an effective appeal. Sometimes, rejection reasons can be vague or misleading. RTI helps you get actual facts and challenge incorrect or unsubstantiated reasons.
File your RTI application with the Public Information Officer (PIO) of the concerned school or the education department. Be specific about the information you seek to avoid delays or unnecessary costs.
However, remember that RTI is not an appeal mechanism itself. It’s a tool to gather information that helps strengthen your formal appeal.
What Documents Do You Need for an RTE Appeal?
When filing an appeal, ensure that all documents that prove your eligibility under RTE provisions are well-organized and readily presented.
Start with a copy of the original rejection letter. This serves as starting evidence of the decision you’re contesting.
Prepare a complete set of RTE eligibility documents. These typically include the child’s age proof, parental income certificate, and residence proof.
If the rejection was related to any specific document, ensure you rectify the problem and provide a corrected version. For instance, if income proof was insufficient, obtain an updated certificate.
Include copies of all previous correspondence with the school. This includes your original application, any follow-up letters, and the rejection notice.
Finally, include your written appeal explaining why the school’s decision was incorrect. Ensure it’s signed and dated, with complete contact information.
Is Legal Help Necessary for RTE Rejection Appeals?
While you can represent yourself throughout the appeal process, legal help can be advantageous, especially in complex or contested cases.
Lawyers specializing in education law or public interest litigation can offer expert advice on your case’s merits and identify any legal violations by the school or authorities.
In cases where a school has a history of discriminatory practices or when a large number of applications are rejected without clear grounds, legal representation may be essential.
Additionally, if your case progresses to a court of law, legal representation becomes mandatory. The court process involves strict procedures that must be followed accurately.
However, for straightforward cases involving simple eligibility issues or documentation errors, self-representation with proper preparation is generally sufficient.
What If Your Appeal Gets Rejected?
Rejection at the formal appeal level can be disheartening, but several avenues remain open.
Approach the State Education Department at a higher level. Some states have a State-level Grievance Redressal Authority or an Appellate Authority where you can file a second-level appeal.
Contact your elected representatives, such as your MLA, MP, or local councilors. Public interest cases often receive attention when highlighted in legislative bodies.
In extreme cases, you can file a writ petition in the High Court or Supreme Court, typically through a public interest litigant or legal aid organization.
Remember, persistence and documentation of all efforts are crucial. Courts recognize that continued efforts to enforce fundamental rights can influence their approach.

Alternative Solutions and Community Support
While navigating the formal appeal process, some alternative solutions can help secure your child’s education.
Approach non-profit organizations working in the education sector in your area. Many focus on helping families whose children are denied RTE admissions.
Community-based organizations often have experience with local authorities and can guide effective interaction with schools and government officials.
Contact other parents facing similar issues. Forming a group can lead to collective action, which is often more effective than individual appeals.
Local media can also be a powerful ally. Responsible reporting of systematic violations can bring public attention that forces action.
Preventing Future Rejections
After resolving your current issue, take steps to prevent future rejections.
Keep your documentation updated and accurate. Income, residence, or age documents that expire must be renewed timely.
Ensure you understand the complete eligibility criteria of each school you apply to. Sometimes, aided schools have different rules than government schools.
Submit applications before the last date. Late applications are one of the most common reasons for rejection.
Maintain complete records of all interactions with the school and education department. This documentation is invaluable if you face future issues.
Read More
How to Find RTE Schools with the Best Facilities: A Complete Parent’s Guide
Can You Apply for RTE If Your Income Exceeds the Limit?
Government Schemes for RTE Graduates: What’s Next?
Conclusion
Rejection of an RTE application can feel like a denial of your child’s basic right to education. However, this should not be the end of the road. The Right to Education Act provides structured mechanisms for addressing grievances, and multiple levels of appeal exist to ensure that every eligible child gets access to quality education.
By understanding the grounds of rejection, filing timely appeals, and using tools like the RTI Act effectively, you can significantly increase your chances of overturning an erroneous decision. While the process may seem daunting, especially for parents without legal or administrative experience, perseverance and proper documentation often yield positive results.
The fundamental right to education is non-negotiable and is designed to ensure a brighter future for every child. Don’t let a procedural hurdle derail that future. By taking informed, timely, and structured steps, you can ensure that this fundamental right is recognized and enforced. Your child’s education and future depend on it.
