
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is essential for businesses aiming to balance profit with positive social and environmental impact. A clear CSR strategy helps companies improve reputation, meet regulatory requirements, and engage stakeholders effectively. Understanding how to implement CSR involves defining goals, integrating sustainable practices, and regularly reporting progress.
This guide covers best practices for CSR, including frameworks for reporting and how CSR differs from ESG (environmental, social, and governance). Businesses can learn how to embed sustainable practices into their operations to create long-term value.
By exploring the benefits of CSR and practical steps for implementation, companies can strengthen their corporate sustainability and meet growing expectations from customers and investors. Knowing the difference between CSR and ESG reporting frameworks also helps guide effective strategy development.
Understanding Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility involves key concepts such as defining what CSR means in a business context, recognizing its fundamental principles, and understanding how CSR differs from Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria. These elements form the foundation for companies to integrate responsible practices effectively.
Defining CSR
Corporate Social Responsibility refers to a company’s commitment to manage its social, environmental, and economic impacts responsibly. It goes beyond compliance with legal obligations to proactive efforts that benefit society and the environment.
CSR initiatives can include reducing carbon emissions, investing in community projects, ensuring fair labor practices, and adopting ethical sourcing. Businesses use CSR to balance profit-making with positive contributions to stakeholders and society.
Implementing CSR helps companies align their operations with broader societal goals, creating shared value for shareholders, employees, customers, and communities.
Core Principles of Corporate Social Responsibility
CSR is guided by principles such as accountability, transparency, ethical behavior, and respect for stakeholder interests. Accountability demands companies take responsibility for their actions and impacts.
Transparency means openly sharing information about business practices and CSR efforts with stakeholders. Ethical behavior involves conducting business fairly and with integrity, avoiding harm to people and the environment.
Respect for stakeholder interests requires considering the needs and rights of employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and shareholders in decision-making. These principles ensure CSR efforts are credible and meaningful.
Difference Between ESG and CSR
ESG and CSR are related but distinct concepts. CSR is a broad approach focusing on voluntary social and environmental responsibilities companies adopt.
ESG refers specifically to measurable criteria used by investors to evaluate a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance. ESG focuses on risk management and long-term value creation linked to sustainability factors.
| Aspect | CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) | ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) |
| Scope | Voluntary social and environmental commitments | Measurable criteria for investment decisions |
| Focus | Ethical practices and stakeholder engagement | Risk assessment and financial performance |
| Audience | Broad stakeholders including society | Investors and financial markets |
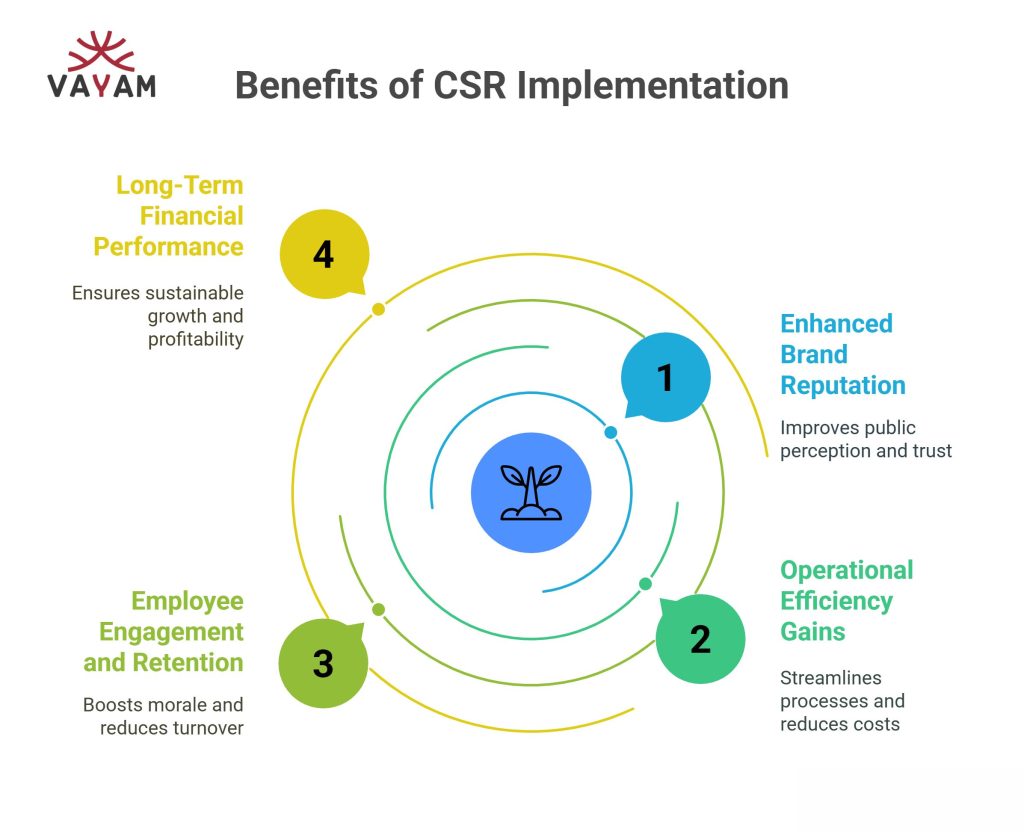
Business Benefits of CSR Implementation
Implementing corporate social responsibility (CSR) can improve a company’s public image, streamline operations, increase employee loyalty, and impact financial outcomes positively. Each area offers tangible advantages that align with both ethical commitments and business objectives.
Enhanced Brand Reputation
A well-executed CSR strategy enhances public perception by demonstrating commitment to social and environmental issues. Consumers increasingly favor companies with transparent, responsible policies. This trust can lead to increased sales and stronger customer loyalty.
Media coverage of CSR initiatives often improves brand visibility, attracting stakeholders who value ethical practices. Businesses that engage with community projects or sustainability efforts distinguish themselves from competitors. This differentiation can open new market opportunities and partnerships.
Operational Efficiency Gains
CSR encourages companies to optimize resource use, reducing waste and lowering costs. Implementing sustainable practices like energy-efficient technologies or supply chain audits leads to measurable savings. These improvements contribute to leaner operations without sacrificing quality.
Waste reduction and recycling programs can decrease disposal fees and regulatory risks. Process improvements made for environmental responsibility often reveal broader operational inefficiencies. The result is a more resilient and cost-effective business model.
Employee Engagement and Retention
Corporate responsibility programs increase employee satisfaction by fostering pride and purpose. Workers involved in CSR activities tend to exhibit higher morale and stronger commitment to company goals. This engagement reduces turnover rates and recruitment expenses.
Employees prefer workplaces where social and environmental values align with their own. CSR initiatives can attract talent looking for meaningful careers. Companies reporting employee volunteerism or sustainability involvement often see improved workplace culture and collaboration.
Long-Term Financial Performance
Sustainable CSR efforts contribute to stable financial returns by building enduring stakeholder relationships. Investors increasingly evaluate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their decisions, influencing company valuations. Responsible companies may access capital at better terms.
Integrating CSR into corporate strategy helps manage risk and anticipate regulatory changes. By reducing environmental and social liabilities, companies protect future earnings. Studies have shown a correlation between CSR performance and consistent profitability over time.
Developing a CSR Strategy
A comprehensive CSR strategy requires precise goals, active communication with key parties, and integration with the company’s core business operations. These elements ensure the strategy is actionable, relevant, and sustainable.
Setting Clear CSR Objectives
Clear objectives guide the CSR efforts and provide measurable outcomes. Companies should focus on specific issues such as reducing carbon emissions, improving labor conditions, or supporting local communities.
Objectives must be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For example, “reduce waste by 30% within two years” is more effective than vague goals like “be more environmentally conscious.”
Defining metrics and benchmarks is crucial. These help track progress and allow adjustments to the strategy based on real data and performance against targets.
Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders builds trust and ensures the CSR strategy addresses relevant concerns. Stakeholders include employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and community representatives.
Methods for engagement can include surveys, focus groups, interviews, and advisory panels. This input identifies priorities and uncovers risks the company may otherwise overlook.
Regular communication and transparency about CSR goals and progress foster stronger relationships. Businesses should also consider stakeholders’ feedback in refining their CSR activities.
Aligning CSR With Business Goals
Effective CSR strategies support and enhance core business objectives. Alignment ensures CSR initiatives contribute to long-term value rather than acting as separate or conflicting efforts.
For instance, a company focused on innovation might prioritize community education programs in STEM fields. A manufacturer might focus on reducing supply chain emissions to cut costs and environmental impact.
This integration must be reflected in resource allocation, leadership involvement, and performance incentives to reinforce the CSR commitment throughout the organization.
How to Implement CSR in Business
Implementing CSR requires a clear understanding of the company’s current efforts, embedding social responsibility into every department, and appointing strong leadership to drive initiatives. These steps form the foundation for a structured and sustainable CSR program.
Assessing Current CSR Initiatives
The first step involves a thorough review of existing CSR activities. This includes evaluating policies, community engagement, environmental practices, and employee programs. Companies should collect data on social and environmental impacts and benchmark against industry standards.
Identifying gaps and strengths enables targeted improvements. Using tools like CSR audits or third-party assessments helps ensure accuracy. The assessment should also measure stakeholder expectations and regulatory compliance to align CSR efforts with external requirements and internal goals.
Integrating CSR Across Departments
CSR must be embedded across functions, from operations and marketing to HR and procurement. Departments need clear roles and responsibilities related to sustainability goals. For example, procurement can focus on ethical sourcing, while HR can lead employee volunteer programs.
Creating cross-departmental teams or committees facilitates collaboration. Communication channels should promote transparency and regular updates on CSR progress. Training programs help staff understand their individual contributions to CSR and reinforce accountability at every level.
Establishing CSR Leadership
Effective CSR implementation demands dedicated leadership. Assigning a Chief Sustainability Officer or CSR manager ensures initiatives receive strategic oversight. This leader coordinates projects, aligns CSR with business objectives, and reports progress to executives and the board.
Leadership also champions a culture of responsibility by engaging employees and external partners. Clear decision-making authority and resource allocation under this role are crucial to sustain momentum and integrate CSR into long-term planning.
Corporate Social Responsibility Best Practices
Effective corporate social responsibility requires clear actions in managing supply chains, engaging with communities, and minimizing environmental impact. These focus areas create measurable value for businesses and stakeholders.
Ethical Supply Chain Management
Companies should ensure transparency and accountability throughout their supply chains. This involves vetting suppliers for labor standards, human rights compliance, and fair wages. Regular audits and certifications, such as Fair Trade or SA8000, help enforce these standards.
Risk assessment tools identify potential ethical issues early. Collaboration with suppliers to improve conditions benefits the whole chain and mitigates reputational risks. Clear communication of expectations and consistent monitoring are essential.
Documenting policies related to child labor, forced labor, and environmental impact fosters credibility. Transparent reporting on supply chain practices enhances stakeholder trust and aligns with broader CSR goals.
Community Engagement Programs
Active investment in local communities strengthens business relationships and supports social development. Initiatives may include educational scholarships, local hiring, infrastructure support, or health services.
Companies should tailor programs to community needs, using stakeholder feedback to guide efforts. Partnering with nonprofits or local governments increases project effectiveness.
Measuring program outcomes with set metrics ensures accountability and improves future initiatives. Communicating these results publicly demonstrates commitment and strengthens the company’s social license to operate.
Environmental Stewardship
Reducing a company’s environmental footprint is central to CSR performance. This includes adopting energy-efficient technologies, waste reduction, and sustainable resource management.
Setting clear targets for carbon emissions, water use, and waste disposal guides actions. Regular environmental audits and reporting against frameworks like the GRI or CDP ensure compliance and transparency.
Implementing circular economy principles, such as product recycling or reuse, reduces environmental impact. Employee training on sustainability practices embeds responsibility throughout the organization.

Sustainable Business Practices Guide
Sustainable business practices focus on reducing environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency. Companies benefit from adopting methods that prioritize responsible resource use, product innovation, and clear environmental policies.
Sustainable Product Development
Developing sustainable products requires integrating environmentally friendly materials and lifecycle thinking from the design phase. Companies should prioritize renewable, recyclable, or biodegradable components and reduce waste during production.
Design choices must also consider energy efficiency and product durability to extend useful life, minimizing environmental strain.
Engaging suppliers with sustainable practices strengthens the product’s overall eco-profile. Certification and compliance with environmental standards further validate the sustainability claims.
Resource Efficiency Initiatives
Efficient resource use cuts costs and lowers environmental footprints. Businesses should focus on optimizing energy consumption through technologies like LED lighting and smart systems.
Water conservation is essential; installing low-flow fixtures and recycling process water reduce waste. Material efficiency, such as minimizing raw input through better process design, decreases excess and cuts expenses.
Tracking resource usage with software tools helps identify inefficiencies and measure improvements over time. Employee training promotes engagement in saving resources daily.
Green Policies and Procedures
Formal green policies establish organizational standards for sustainability efforts. They often address waste management, emissions reduction, and eco-friendly procurement.
Clear procedures ensure consistent application of these policies, from office recycling programs to supplier assessments for environmental compliance.
Regular audits verify adherence, while transparent reporting fosters accountability internally and externally. Embedding sustainability into corporate culture encourages ongoing commitment and innovation.
Corporate Sustainability Guide
Corporate sustainability requires a clear plan, consistent measurement of progress, and integration into company culture. Success depends on aligning goals with practical actions and engaging employees at all levels.
Developing a Sustainability Roadmap
A sustainability roadmap identifies specific environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals tied to the business strategy. It begins with assessing current impacts, setting measurable targets, and defining timelines.
Key steps include:
- Conducting a materiality assessment to prioritize issues
- Aligning goals with industry standards and regulations
- Defining short-term and long-term objectives
- Assigning responsibilities to departments or teams
The roadmap should be flexible enough to adapt as regulations evolve or new challenges emerge. Clear documentation and communication ensure all stakeholders understand their roles.
Measuring Sustainability Performance
Tracking sustainability requires selecting relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with the roadmap. These may include carbon footprint, energy use, waste reduction, and diversity metrics.
Effective measurement involves:
- Establishing baseline data
- Using recognized standards like GRI or SASB for reporting
- Regular audits and progress reviews
- Transparent reporting to stakeholders
Data accuracy is critical. Companies use tools like sustainability software or third-party verification to maintain credibility. Metrics should drive continuous improvement, not just compliance.
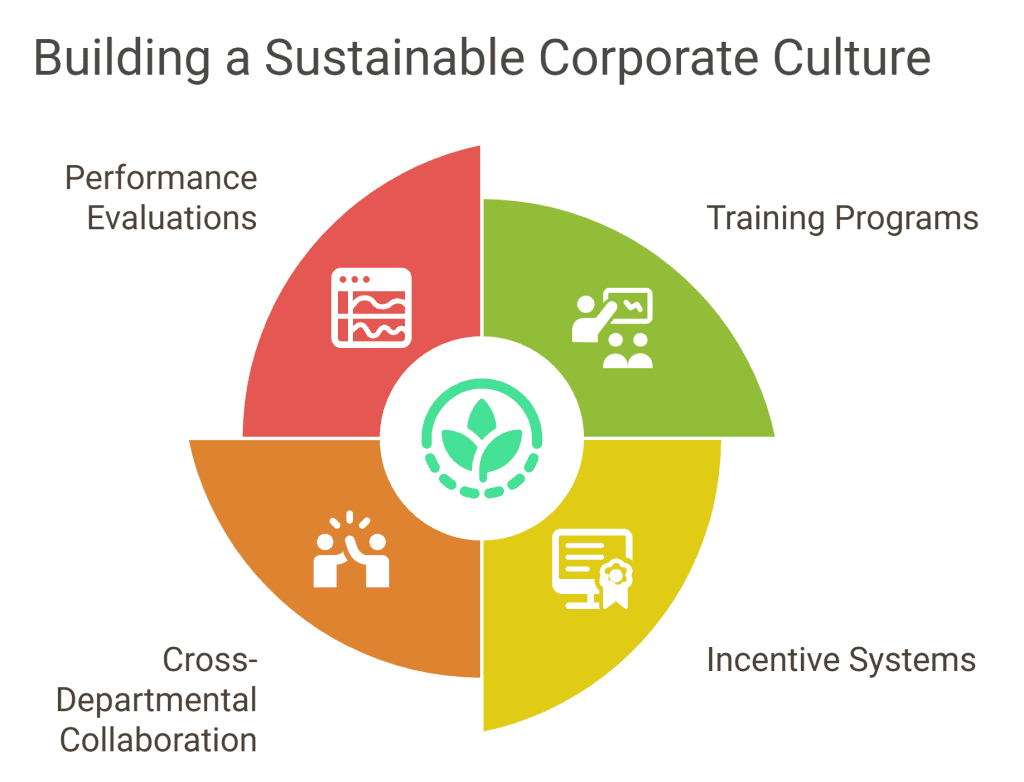
Corporate Culture and Sustainability
Embedding sustainability into corporate culture encourages employee participation and innovation. Leadership must demonstrate commitment through policies, resource allocation, and communication.
Strategies to build this culture include:
- Training programs on sustainability principles
- Incentive systems that reward sustainable practices
- Encouraging collaboration across departments
- Incorporating sustainability goals into performance evaluations
A strong culture aligns values across the organization, making sustainability a core driver rather than a peripheral task.
CSR Reporting Framework Guide
Effective CSR reporting relies on recognized standards, clear performance metrics, and honest disclosure practices. These elements help organizations communicate their social and environmental impacts accurately to stakeholders.
Global Reporting Standards
Global reporting standards provide a consistent basis for CSR disclosures. The most widely used frameworks include the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
The GRI focuses on broad sustainability impacts, covering economic, environmental, and social factors. SASB targets financially material issues specific to industries, making it relevant for investors. TCFD emphasizes climate-related risks and opportunities in financial reporting.
Organizations should select a framework that aligns with their industry, stakeholder expectations, and reporting goals. Using recognized standards ensures credibility and facilitates benchmarking against peers.
Selecting Key Performance Indicators
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) must be measurable, relevant, and tied directly to a company’s CSR objectives. Common KPIs include carbon emissions, water usage, employee diversity rates, and community investment amounts.
Choosing the right KPIs requires understanding which social and environmental impacts the business can influence most. They should also reflect stakeholder priorities and regulatory requirements.
KPIs can be quantitative or qualitative but must be reported consistently over time. This consistency allows tracking progress and highlights areas needing improvement.
Transparency and Disclosure
Transparency in CSR reporting means providing clear, honest, and complete information about policies, practices, and outcomes. Companies should disclose both positive results and challenges.
Details to disclose include methodology, data sources, assumptions, and any third-party verification processes. Transparency builds stakeholder trust and reduces the risk of reputational damage.
Reports should be accessible, avoiding jargon and complex language. Visual aids such as charts and tables can improve clarity and help stakeholders understand performance data.
Read More
How to Gain Attention of CSR-Focused Brands for Your NGO?
The #1 Strategy for Turning CSR into Recurring Donations
7 Corporate CSR Success Stories That Every NGO Should Learn From
Monitoring and Improving CSR Performance
Effective CSR management requires regular evaluation of outcomes, ongoing refinement of strategies, and active incorporation of internal and external feedback. These actions ensure that a company’s social and environmental commitments stay relevant and produce measurable results.
Conducting Impact Assessments
Impact assessments measure how CSR initiatives affect stakeholders, the environment, and the community. Companies should define clear indicators aligned with CSR goals, such as carbon footprint reduction, employee well-being, or community development.
Regular data collection and analysis help identify successes and gaps. Quantitative metrics (e.g., emissions saved, funds donated) combined with qualitative insights (e.g., stakeholder interviews) create a fuller picture of impact.
The assessment can be internal or involve third-party auditors for impartiality. Documenting findings supports transparency and informs future CSR decisions.
Continuous Improvement Processes
Continuous improvement means regularly reviewing CSR activities to enhance effectiveness. Companies often establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and set review cycles—quarterly or annually—to track progress.
Adjustments may include reallocating resources, updating policies, or adopting new technologies. Employee training and leadership engagement are critical to driving these changes.
Using frameworks such as PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) encourages systematic testing and refinement. The goal is to evolve CSR efforts in response to changing business, social, and environmental conditions.
Collecting and Utilizing Feedback
Feedback from employees, customers, suppliers, and communities provides valuable insights into CSR performance. Methods include surveys, focus groups, suggestion boxes, and stakeholder meetings.
It is essential to analyze feedback carefully and prioritize concerns linked to CSR objectives. Transparent communication about how feedback influences decisions increases trust and stakeholder buy-in.
Feedback loops should be ongoing rather than one-time events, ensuring CSR programs remain responsive and adaptive to real-world impacts and expectations.
